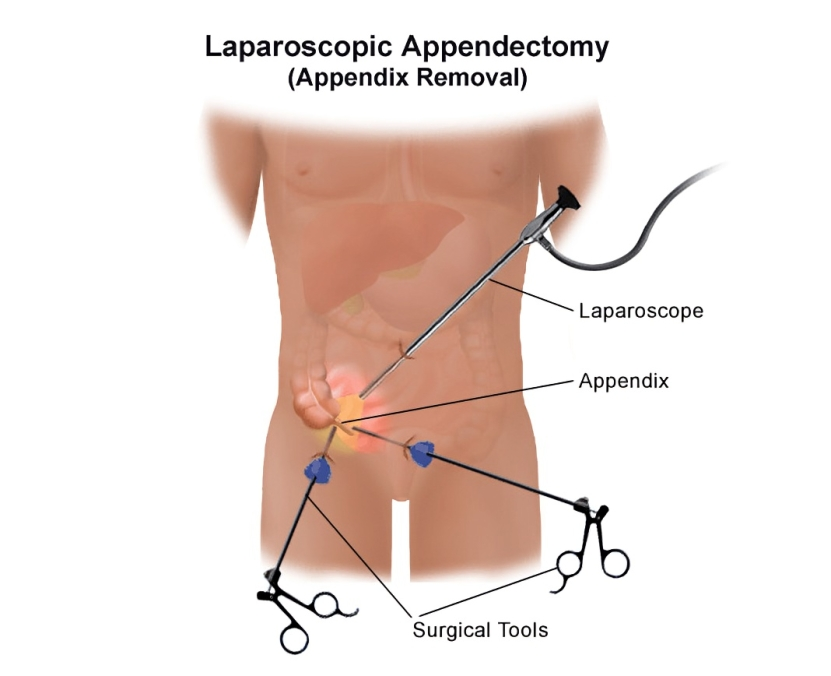
Laparoscopic Appendectomy: A Minimally Invasive Approach to Appendicitis Treatment.
Appendicitis, characterized by inflammation of the appendix, is a common medical emergency that often requires surgical intervention. Traditionally, open appendectomy was the standard procedure for removing the inflamed appendix. However, in recent decades, laparoscopic appendectomy has emerged as a preferred and minimally invasive alternative. This article explores the key aspects of laparoscopic appendectomy, including its procedure, benefits, and recovery.
Understanding Appendicitis
The appendix is a small, pouch-like organ located in the lower right abdomen. When it becomes inflamed, typically due to a blockage, it can lead to a condition known as appendicitis. Common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. If left untreated, an inflamed appendix can rupture, posing serious health risks.
Laparoscopic Appendectomy Procedure
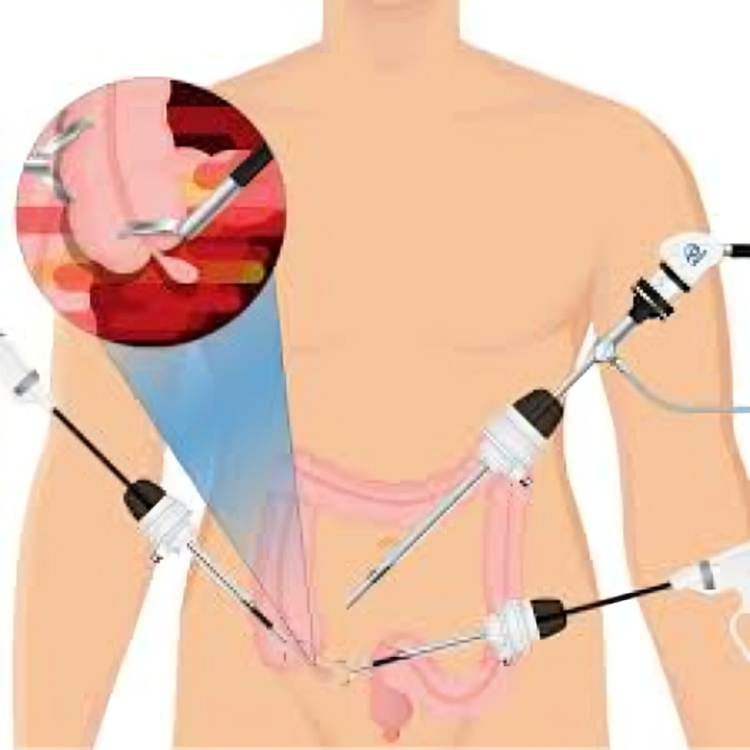
Laparoscopic appendectomy involves the use of small incisions and a thin, flexible tube with a camera (laparoscope) to visualize the appendix and surrounding tissues. The surgical instruments are inserted through additional small incisions, allowing the surgeon to remove the inflamed appendix with precision. The procedure typically follows these key steps:
- Anesthesia: The patient is administered general anesthesia to ensure they are unconscious and pain-free throughout the surgery.
- Incisions: Three to four small incisions are made in the abdomen to accommodate the laparoscope and surgical instruments.
- Visualization: The laparoscope is inserted through one of the incisions, providing the surgeon with a clear view of the appendix and surrounding structures on a monitor.
- Appendectomy: Surgical instruments are introduced through the other incisions, allowing the surgeon to carefully dissect and remove the inflamed appendix.
- Closure: The small incisions are closed with stitches or surgical glue, and a bandage is applied.
Benefits of Laparoscopic Appendectomy
- Minimally Invasive: Laparoscopic appendectomy involves smaller incisions compared to open surgery, resulting in less trauma to the abdominal muscles and tissues.
- Faster Recovery: Patients often experience a quicker recovery and shorter hospital stays with laparoscopic appendectomy compared to open surgery.
- Reduced Pain: The smaller incisions and minimized tissue disruption contribute to less postoperative pain, requiring less pain medication.
- Cosmetic Advantage: The smaller scars associated with laparoscopic surgery are generally more cosmetically appealing than the larger incision used in open appendectomy.
- Lower Infection Risk: Smaller incisions and reduced exposure of internal organs decrease the risk of postoperative infections.
Recovery and Postoperative Care
Patients undergoing laparoscopic appendectomy typically experience a faster recovery than those who undergo open surgery. Most can resume normal activities within a few days to a week. Postoperative care may involve pain management, monitoring for signs of infection, and gradually reintroducing regular activities under the guidance of the surgeon.
Conclusion
Laparoscopic appendectomy represents a significant advancement in the treatment of appendicitis, offering patients a minimally invasive alternative with numerous benefits. As technology continues to evolve, laparoscopic procedures are becoming increasingly standard in various surgical interventions, providing patients with faster recovery times, reduced pain, and improved cosmetic outcomes. Individuals experiencing symptoms of appendicitis should seek prompt medical attention, and those considering surgery should consult with their healthcare providers to explore the most suitable treatment options based on their specific needs and circumstances.